Lab 8:Community Interactions
Images Credit: Dr. Wesley Dubbs
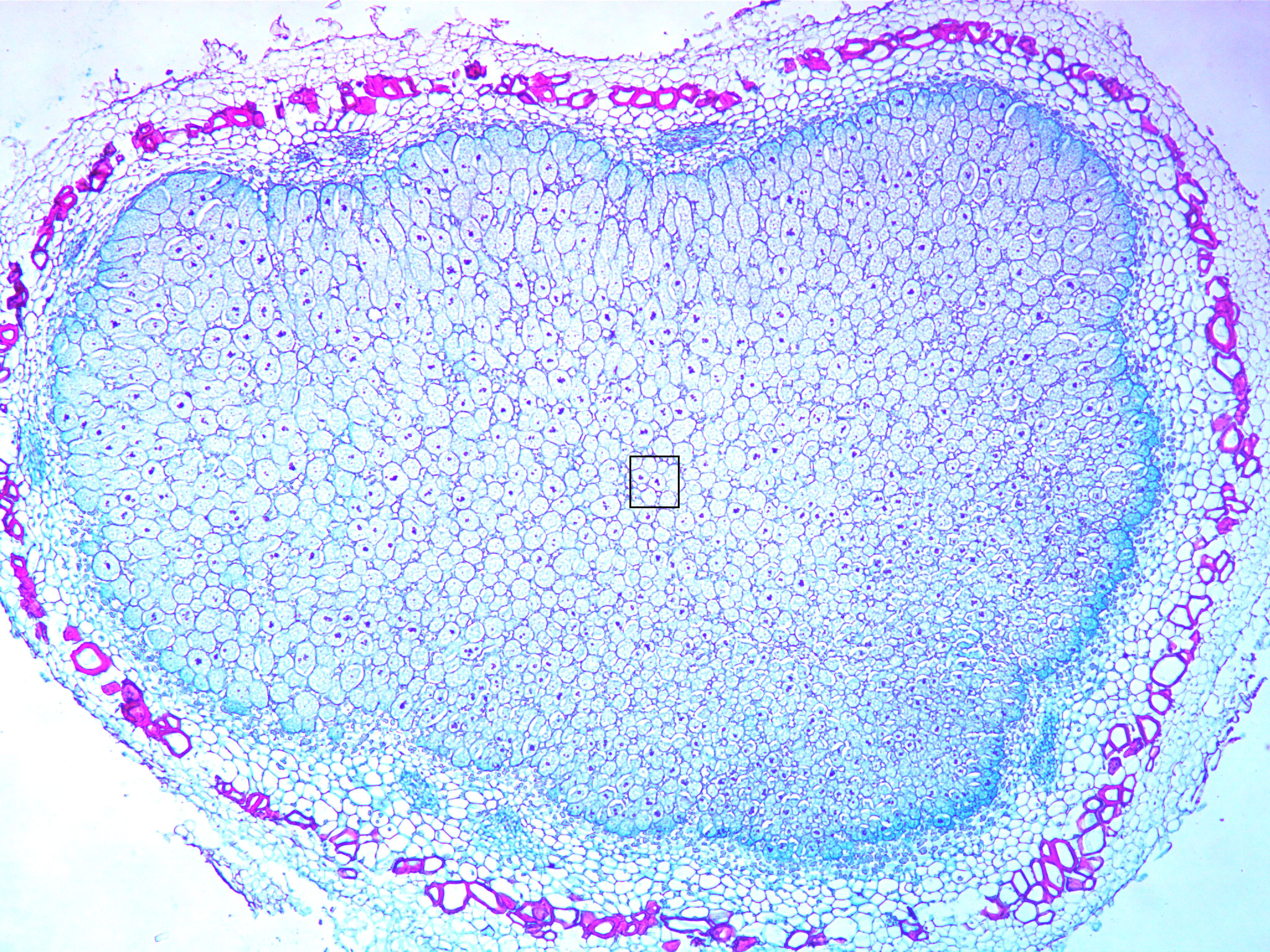
Low magnification soybean root nodule cross section (40X total magnification):
Soybean root nodule containing nitrogen fixing Rhizobium bacteria.
Note the blue-stained central core of nitrogen fixing soybean plant cells “infected” with Rhizobium bacteria surrounded by the peripheral uninfected cortex (C).
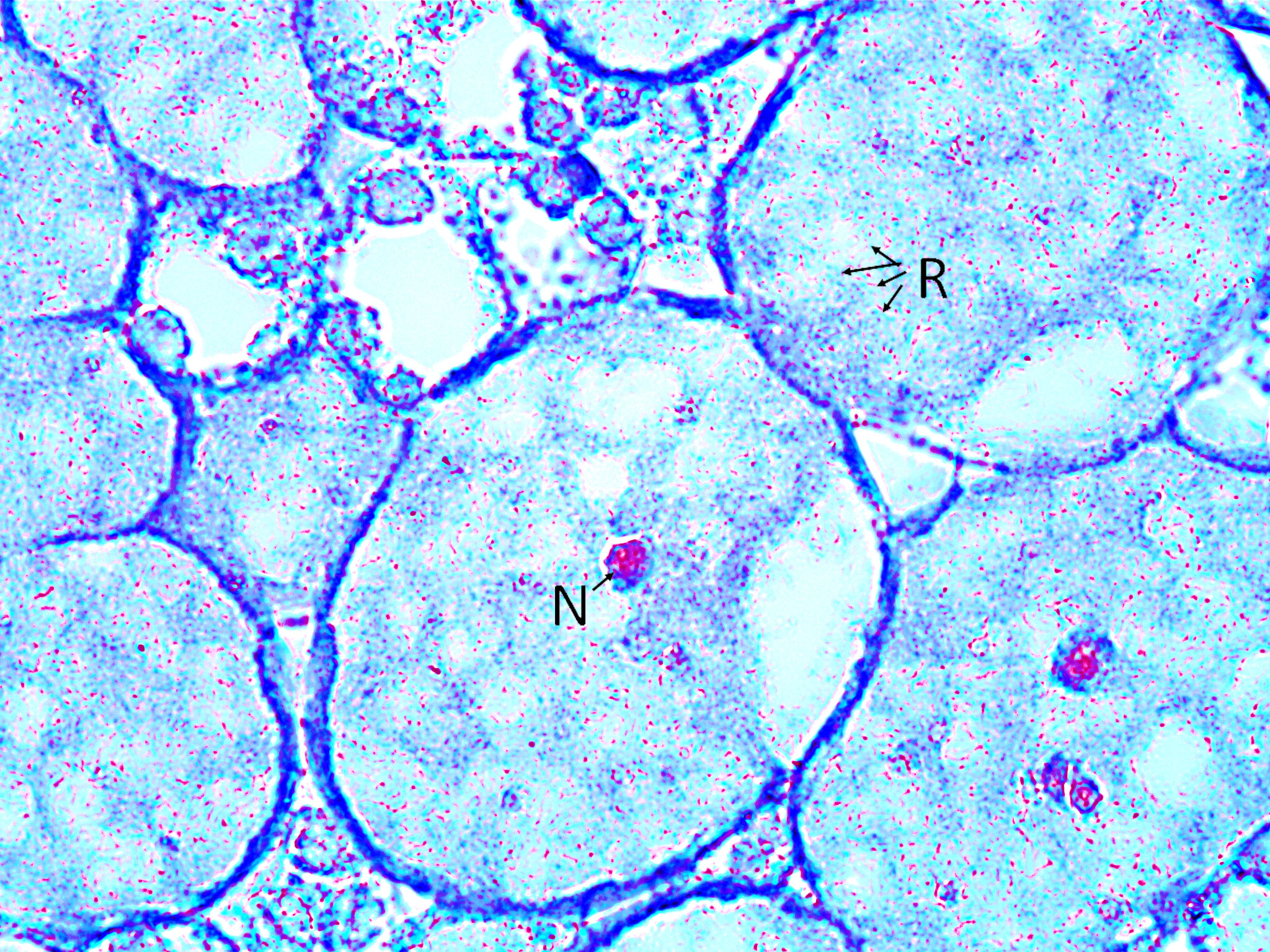
High magnification soybean root nodule cross section (1000X total magnification):
Soybean root cells containing nitrogen fixing Rhizobium bacteria. Note the plant cells containing a single nucleus (N) and the many many tiny Rhizobium bacteria, stained red (R).
———–
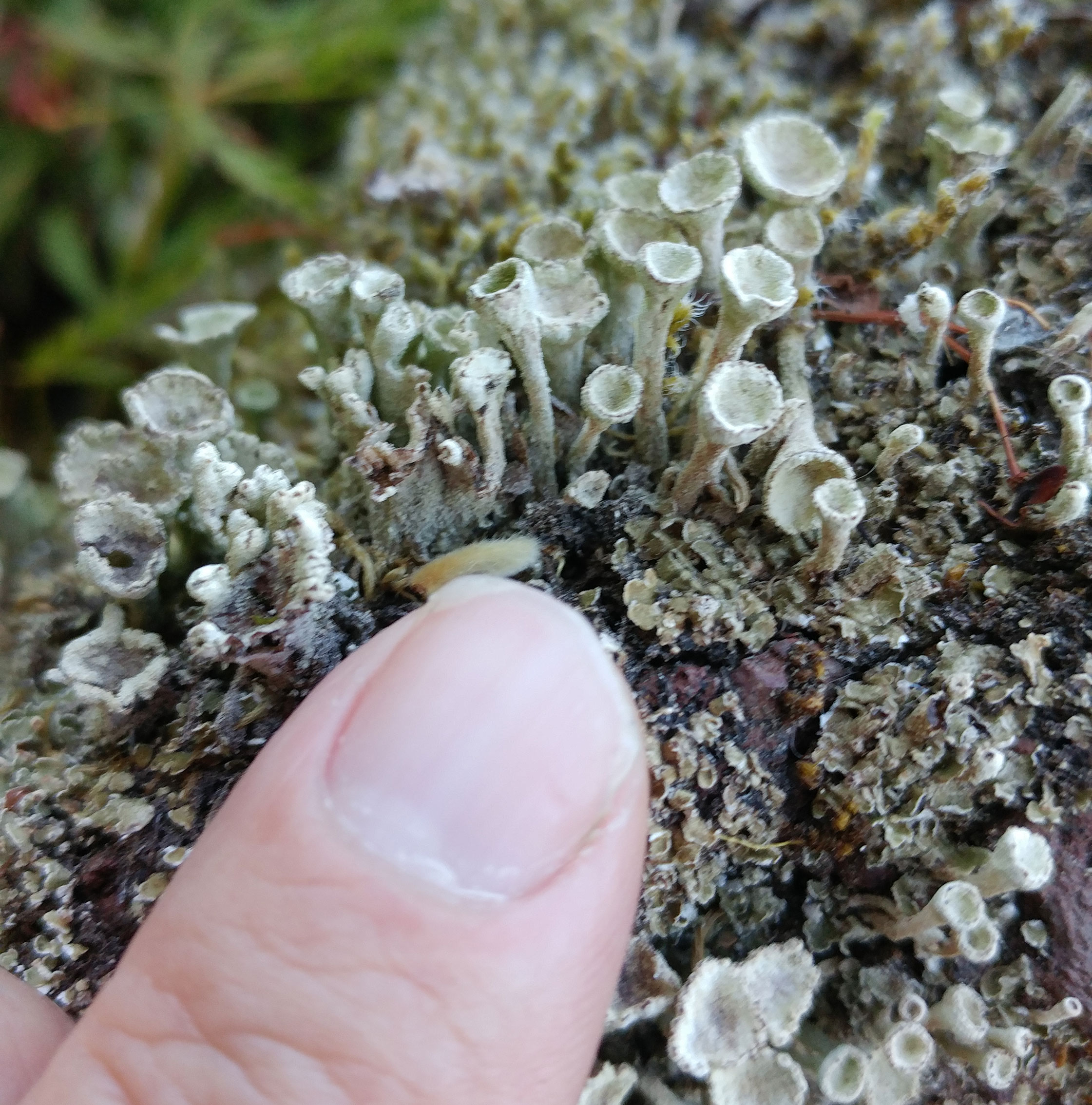
Lichen fruiting body (Cladonia spp.):
Note the small cup shaped structures that produces the reproductive spores for the fungus portion of the lichen.

———
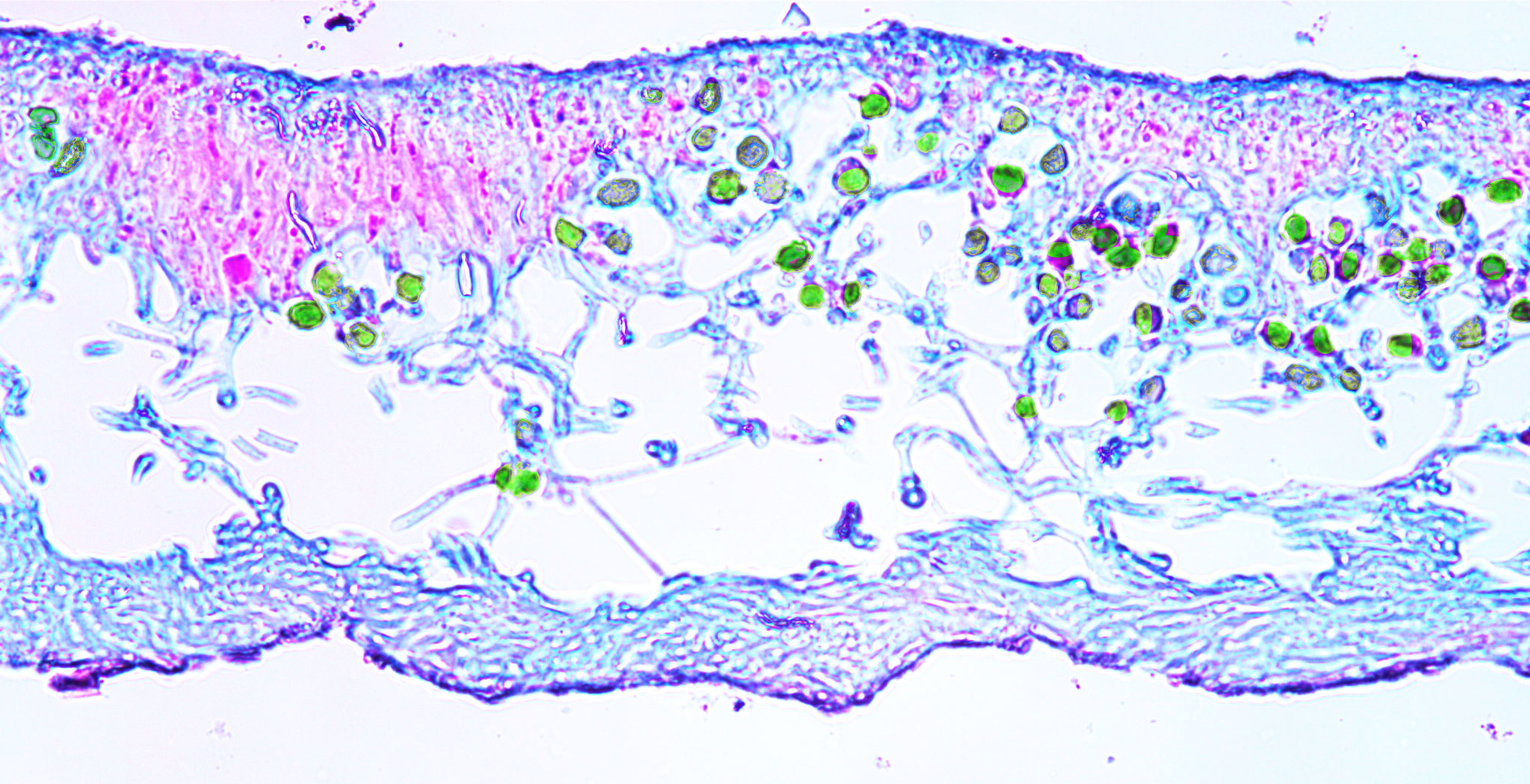
Physcia lichen (400X total magnification):
Physcia lichen thallus cross section. Note the cells of the fungi (stained purple/pink) and those of the algae (green).
———-
Termite Gut Symbionts (100X total magnification):
Contents from a termite gut. Note the large cells of the genus Trichonympha, the most common type of flagellate in the termite gut. Note those organisms with nuclei (N)
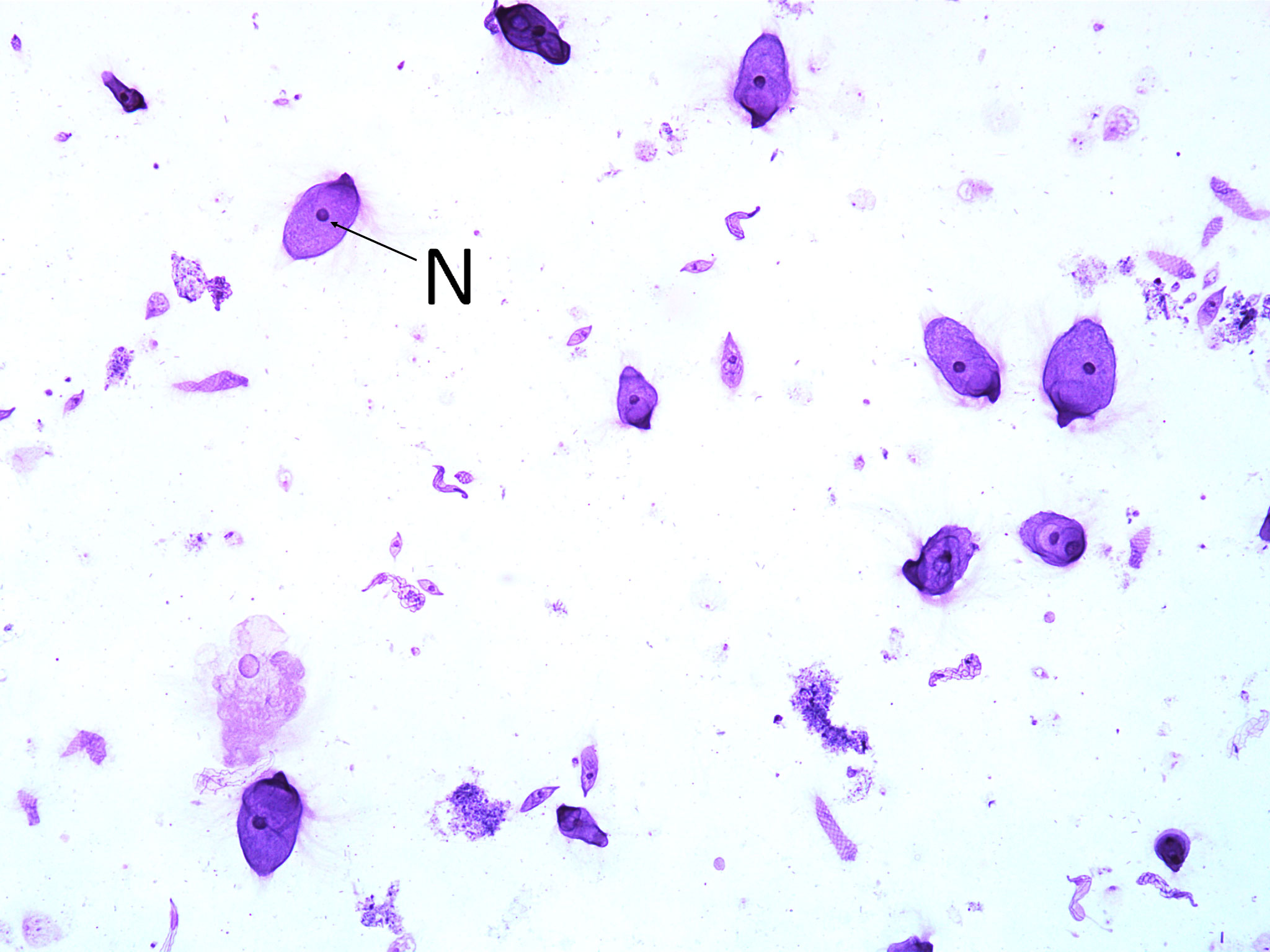
———
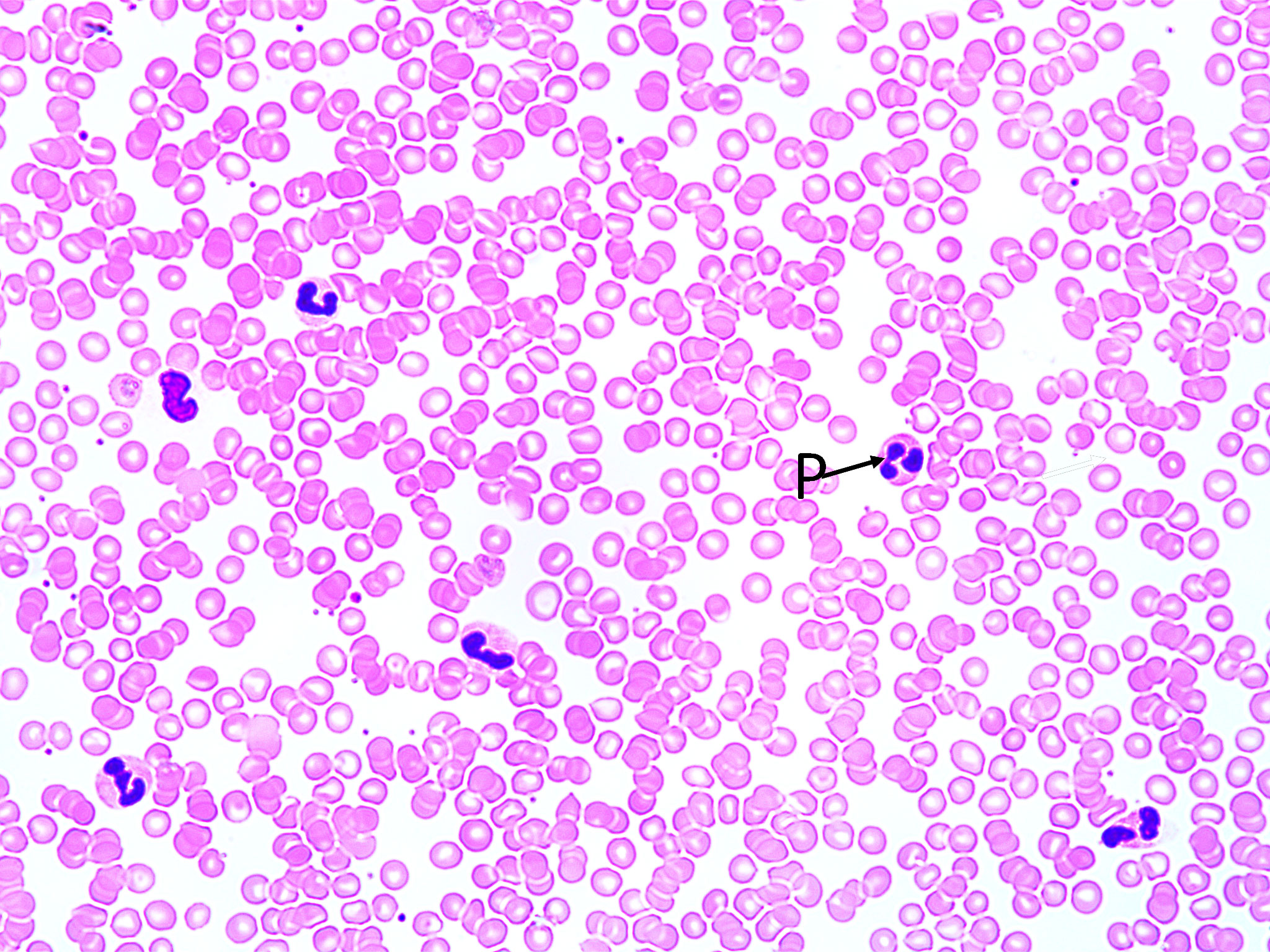
Human Red Blood Cells. Some containing Plasmodium (400X total magnification):
Note the “regular” red blood cells which lack nuclei. Also note the red blood cells infected with the protist Plasmodium (P). Plasmodium is the causative agent of malaria.